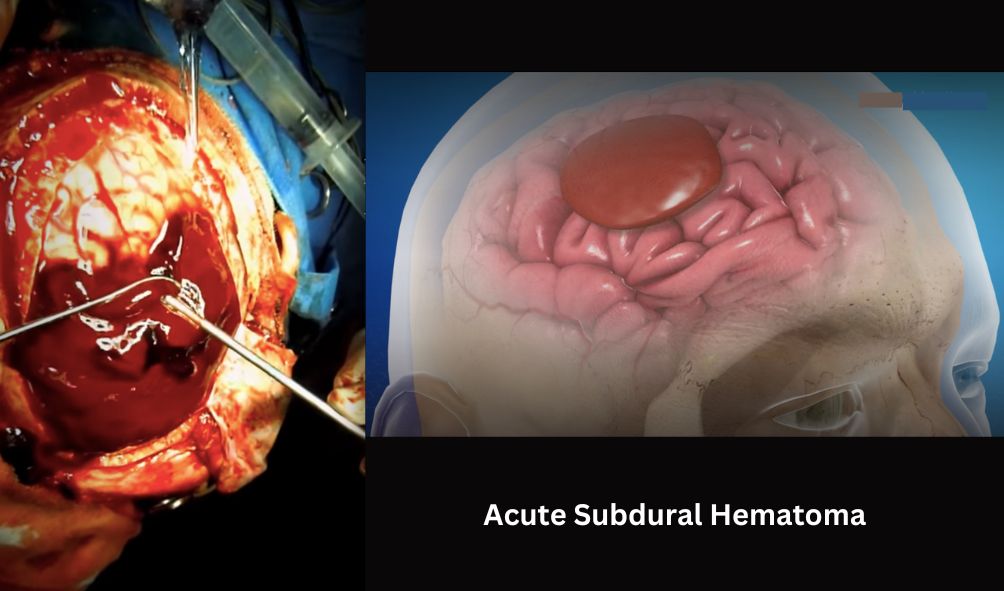
What is Acute Subdural Hematoma ?
Acute subdural hematoma is a serious condition where blood collects between the brain and its outer covering, called the dura mater. This usually happens as a result of a head injury or trauma, causing blood vessels to rupture and blood to accumulate in this space. Acute subdural hematoma may sound like a complex term, but let’s break it down into simpler terms to understand what it means and why it’s important. This condition is a type of brain injury that requires attention and understanding for better awareness and prevention.
Causes and symptoms of Acute subdural hematoma
The most common cause of acute subdural hematoma is a severe blow to the head, such as those sustained in car accidents, falls, or other traumatic incidents. Older individuals and people with certain medical conditions may be more susceptible to this condition due to weakened blood vessels.
Symptoms:
Recognizing the symptoms of acute subdural hematoma is crucial for early detection and treatment. These symptoms may include:
- Headache: Persistent and severe headaches that worsen over time.
- Confusion: Difficulty in vision, speech and understanding or processing information.
- Nausea and vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach and vomiting.
- Drowsiness or unconsciousness: Extreme tiredness or loss of consciousness.
- Unequal pupil size: One pupil may appear larger than the other.
Treatment and preventions of Acute subdural hematoma
Immediate medical attention is necessary for anyone suspected of having an acute subdural hematoma. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the accumulated blood and relieve pressure on the brain. Medications may also be administered to manage pain and prevent further complications.
Preventions:
While accidents are not always avoidable, taking precautions can help reduce the risk of head injuries:
- Wear seat belts: Always use seat belts while driving or riding in a vehicle.
- Helmet use: Wear helmets during activities like biking, skating, or participating in contact sports.
- Prevent falls: Use handrails and non-slip mats to reduce the risk of falling, especially in older adults.
Understanding acute subdural hematoma in simple terms is essential for promoting awareness and taking preventive measures. By recognizing the signs, seeking prompt medical attention, and taking precautions to prevent head injuries, we can contribute to a safer environment for ourselves and those around us. Always prioritize safety to protect the precious organ that is our brain.